USA Immigration
Are you interested in immigrating to the United States or want to sponsor someone? The United States provides immigrant visas based on family ties, employment, adoption, special immigrant categories, and the diversity visa.
H1-B: WORK VISA
The H1-B visa is a non-immigrant visa that allows U.S. companies to employ foreign workers in specialty occupations that require theoretical or technical expertise. Here’s an overview of the H1-B visa process and key points:
Key Points of the H1-B Visa
- Eligibility Requirements:
- Specialty Occupation: The job must require specialized knowledge and a minimum of a bachelor’s degree or its equivalent.
- Beneficiary Qualifications: The prospective employee must have at least a bachelor’s degree in a field related to the job. Equivalent work experience can also be considered.
- Employer Sponsorship:
- The U.S. employer must sponsor the foreign worker by filing a petition with the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS).
- Employers must obtain a Labor Condition Application (LCA) from the Department of Labor, attesting that they will pay the prevailing wage and provide working conditions that will not adversely affect other similarly employed workers.
- Cap and Lottery System:
- There is an annual cap of 65,000 H1-B visas, with an additional 20,000 visas available for workers with a master’s degree or higher from a U.S. institution.
- If the number of petitions exceeds the cap, a lottery system is used to select the petitions that will be processed.
- Validity Period:
- The H1-B visa is initially valid for three years and can be extended for up to six years. Further extensions are possible under certain conditions, such as if the worker is pursuing a green card.
- Dual Intent:
- The H1-B visa allows for dual intent, meaning the visa holder can apply for and pursue permanent residency (green card) while on H1-B status.
- Dependents:
- H1-B visa holders can bring their spouse and children (under 21 years old) under the H4 visa category. H4 visa holders can attend school, but generally, they cannot work unless they obtain an Employment Authorization Document (EAD) under specific conditions.
Application Process
- Labor Condition Application (LCA)
- The employer files an LCA with the Department of Labor, detailing the working conditions and wages for the H1-B employee.
- Petition Filing
- The employer files Form I-129 (Petition for a Non-immigrant Worker) with the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), along with the required fees and supporting documents, such as the approved LCA and proof of the worker’s qualifications.
- Visa Processing
- If the petition is approved, the worker can apply for the H1-B visa at a U.S. consulate or embassy in their home country. This includes submitting Form DS-160, scheduling a visa interview, and paying the visa application fee.
- Entry to the U.S.
- Once the visa is granted, the worker can enter the U.S. to begin employment. They must present their visa and supporting documents to the Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officers at a U.S. port of entry.
Conclusion
The H1-B visa is a crucial pathway for U.S. employers to access highly skilled foreign talent. The process is highly regulated, requiring employers and employees to meet specific criteria and follow precise procedures.
B1: Business Visa

The United States, a global hub for commerce, attracts millions of business visitors annually. The US B1 Business Visa facilitates short-term business travel to the US, allowing individuals to engage in various business activities without actively managing a business.
Overview of the B1 Business Visa
The US B1 Business Visa is designed for individuals visiting the US for business purposes. Typically issued for 6-12 months, it supports activities such as attending conferences, conducting negotiations, and participating in meetings. This visa is crucial for businesspeople and executives who need to travel to the US for short-term business engagements.
Key Activities Permitted Under the B1 Visa
- Conducting Negotiations: Facilitates business negotiations and discussions.
- Sales or Investment Meetings: Allows participation in sales or investment meetings.
- Discussing Planned Investments or Purchases: Enables discussions related to planned investments or business purchases.
- Business Investment Purposes: Permits business investment activities.
- Attending Meetings: Supports attendance at various business meetings.
- Interviewing and Hiring Staff: Allows interviewing and hiring of potential employees.
- Research Purposes: Enables conducting business-related research.
Eligibility Requirements for the B1 Business Visa
To be eligible for the B1 visa, applicants must meet specific requirements:
- Business Purpose: The visit must be for business purposes only.
- Financial Support: Applicants must have sufficient funds to support themselves during their stay.
- Intent to Leave: Applicants must intend to leave the US upon visa expiration.
Required Documentation for the B1 Visa Application
While the documentation requirements for the B1 visa are not as stringent as other visa types, the following documents are typically required:
- Valid Passport: Must be valid for the duration of the stay.
- Proof of Funds: Evidence of financial means to support the stay.
- Support Letters: Letters supporting the business purpose of the visit.
- Employer Letter: If traveling as an employee, a letter from the employer is required.
- Business Ownership Proof: For business owners, proof of business ownership is necessary.
- Insurance and Other Documents: Travel insurance and other supporting documents.
Application Process for the B1 Business Visa
The application process for the US B1 Business Visa involves several steps:
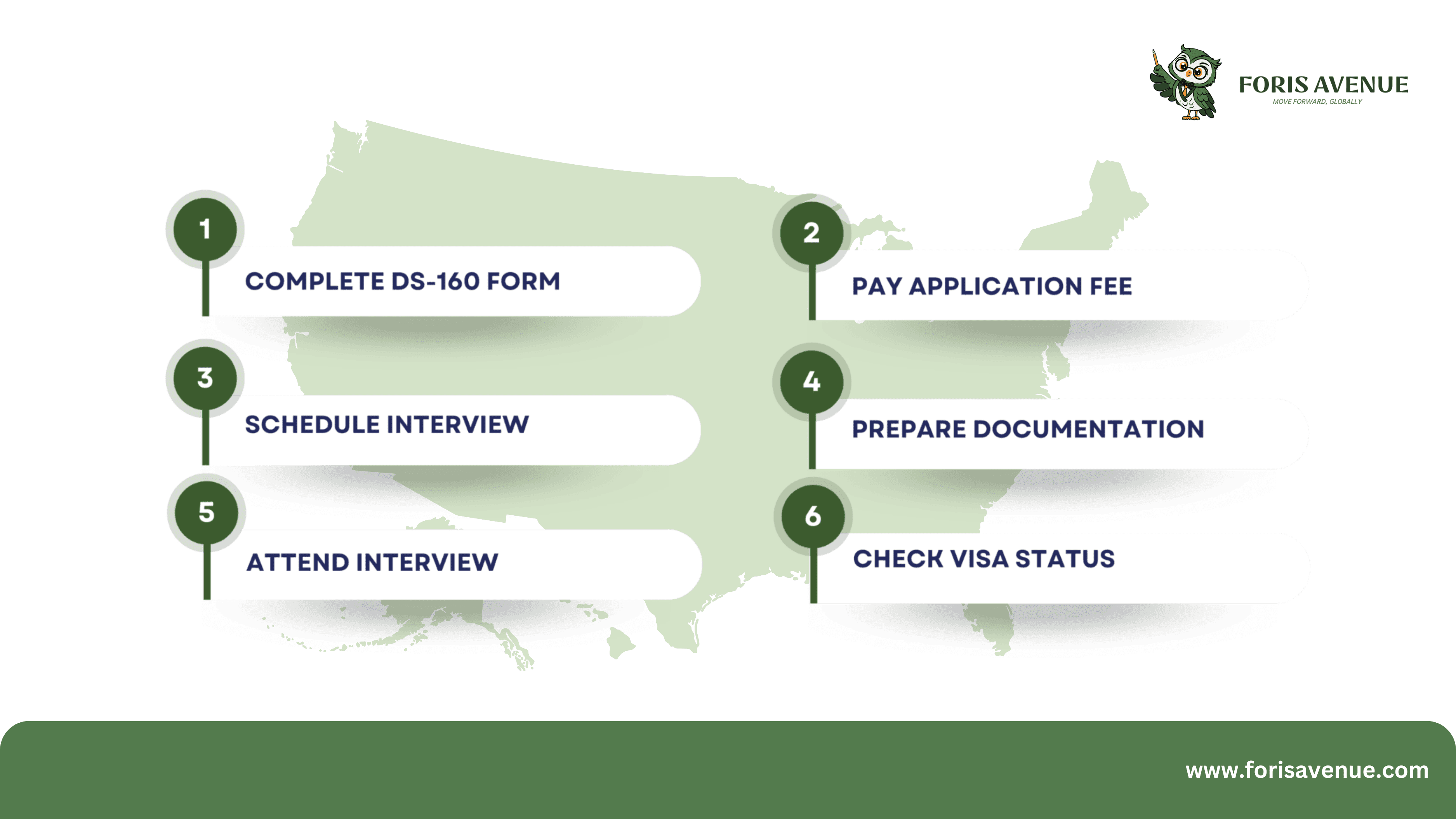
- Complete DS-160 Form: Fill out the DS-160 form online.
- Pay Application Fee: Pay the B1 visa application fee of $185.
- Schedule Interview: Make an appointment for the visa interview.
- Prepare Documentation: Gather all required documents for the application.
- Attend Interview: Participate in an interview with a consular officer.
- Check Visa Status: Check the status of the visa on the attached passport.
Benefits of the B1 Business Visa
- Visa-Free Travel: Allows visa-free travel to 50 countries.
- Short-Term Training: Allows to participate in short-term training programs.
- Conferences and Seminars: Allows to attend conferences, seminars, and business events.
- Multiple Entries: Allows multiple entries into the US.
Cost of the B1 Business Visa
The application fee for the US B1 Business Visa is $185. Additional costs may include travel insurance and other related expenses.
How We Can Assist You
Our team can help streamline your B1 visa application process, offering end-to-end support and leveraging our extensive knowledge of US immigration programs. We ensure that your application is prepared and filed efficiently, increasing your chances of obtaining the visa quickly.
F1: Student Visa

The United States stands as a beacon for international students seeking a world-class education. Known for its prestigious universities and diverse academic offerings, the USA provides unparalleled opportunities for students from around the globe.
Why Choose the USA for Education?
Global Recognition and High Academic Standards
The USA is renowned for its high academic standards and rigorous accreditation processes, ensuring that degrees earned are recognized and respected worldwide. American universities are consistently ranked among the best in the world, making a degree from the USA a valuable asset in the global job market.
Diverse Range of Programs and Degrees
From liberal arts colleges to specialized technical institutes, the USA offers a wide range of programs and degrees to cater to diverse interests and career goals. Whether you are interested in humanities, sciences, business, or technology, you will find a program that suits your aspirations.
Innovative Learning Environments
American universities emphasize experiential learning through practical lectures, smaller class sizes, and interactive discussions. This approach helps students gain a deep understanding of their subjects and develop critical thinking skills.
Rich Cultural Experience
Studying in the USA offers a unique cultural experience, allowing you to interact with people from different backgrounds and participate in a vibrant campus life. This cultural diversity enhances your educational experience and broadens your global perspective.
Top Industries in the USA
The USA is home to a diverse array of industries, providing ample job opportunities for graduates. Some of the leading industries include:
- Petroleum
- Steel
- Motor Vehicles
- Aerospace
- Computer Technology
- Telecommunications
- Chemicals
- Electronics
- Food Processing
- Pharmaceuticals
- Consumer Goods
- Lumber and Mining
- Agriculture
With such a robust industrial base, graduates can find opportunities in various sectors, enhancing their career prospects.
Living and Working as a Student in the USA
Part-Time Employment
International students with F1 status can work on-campus for up to 20 hours per week during academic sessions and full-time during scheduled breaks. Off-campus employment is possible after the first academic year with proper authorization.
Sports and Extracurricular Activities
Students can engage in various sports and extracurricular activities, fostering a well-rounded educational experience. Popular sports include American Football, Basketball, Soccer, and Tennis.
Student Intakes
The USA offers multiple intakes throughout the year, allowing flexibility in choosing your start date:
- Spring Intake: January
- Summer Intake: May
- Fall Intake: September
Academic Breaks
Students enjoy breaks during:
- Winter Break: December (4-6 weeks)
- Spring Break: March/Early April (4 weeks)
Levels of Education in the USA
Associate Degree
A two-year program offered by community colleges, often serving as a stepping stone to a bachelor’s degree. Types of associate degrees include:
- Associate of Arts (AA)
- Associate of Science (AS)
- Associate of Applied Science (AAS)
Bachelor’s Degree
A four-year undergraduate program offered by universities and colleges. It allows students to specialize in a field of their choice.
Master’s Degree
A one to two-year program post-bachelor’s degree, focusing on advanced studies in a specific field. Requires a bachelor’s degree for admission.
Doctoral Degree (PhD)
A three to six-year program requiring completion of a master’s degree. In some cases, students can enter a doctoral program directly after a bachelor’s degree.
Popular Programs for International Students
American universities offer a wide array of programs, with some of the most popular fields being:
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- Business Administration
- Mathematics and Physical Sciences
- Social Sciences
- Education
- Fine and Applied Arts
Types of Study Visas
- F1 Visa: For students enrolled in a full-time academic program.
- M1 Visa: For students attending vocational or technical schools.
- J1 Visa: For students in exchange programs.
Additional Visa Services
- B1/B2 Visa: Non-immigrant visas for business (B1) and tourism (B2). Can be combined for both purposes.
- F2 Visa: Dependent visa for spouses and children of F1 visa holders.
Benefits of Studying in the USA
Studying in the USA offers numerous benefits:
- Access to top-ranked institutions
- High-quality education and innovative teaching methods
- Wide range of scholarships and financial aid
- Opportunities for research and academic flexibility
- Exposure to cultural diversity and international lifestyles
- Pathways to employment in leading global companies
- Potential for citizenship through work opportunities following graduation
US Education System
The US education system is designed to foster academic excellence through a combination of:
- Lectures
- Discussions
- Practical Applications
- Case Studies
- Experiential Learning
Student performance is continuously assessed through participation, quizzes, tests, lab work, assignments, and presentations.
Scholarships in the USA
Numerous scholarships are available for international students, reducing the financial burden of studying abroad:
- Academic Scholarships: Based on academic performance.
- Sports Scholarships: For students excelling in sports.
- Average Academic Scholarships: Based on overall performance, including extracurricular activities.
- Need-Based Scholarships: For students from low-income backgrounds.
- Country-Based Scholarships: For students from developing countries.
- University Scholarships: Entrance-based scholarships funded by universities.
- Privately Funded Scholarships: Sponsored by private entities and alumni.
- Government-Funded Scholarships: Provided by the US government to promote educational globalization.
Post Graduate Work Permit (PGWP)
International students can obtain a Post Graduate Work Permit (PGWP) of up to 24 months after graduation, with extensions available for Optional Practical Training (OPT).
CPT and OPT
Curricular Practical Training (CPT)
Allows F1 students to gain work experience through internships and employment related to their field of study.
Optional Practical Training (OPT)
Permits F1 students to work in their field of study after graduation. OPT can be:
- Pre-Completion: Part-time or full-time work before graduation.
- Post-Completion: Part-time or full-time work after graduation.
Types of Institutions in the USA
- Public Universities: Funded by state governments and offering a wide range of programs.
- Private Universities: Funded through private sources and known for their high academic standards.
- Technical Institutes: Specialize in technological research and offer short-term programs.
- Community Colleges: Offer two-year associate degree programs and serve as a pathway to four-year universities.
Notable Institutions
The USA is home to many prestigious institutions, including Ivy League universities such as:
- Brown University
- Columbia University
- Cornell University
- Dartmouth College
- Harvard University
- University of Pennsylvania
- Princeton University
- Yale University
The step-by-step process to apply for a study visa in the US
- First, choose the desired program and shortlist the university of your choice which offers the program you look for.
- Appear for any of the English language proficiency tests like IELTS, TOEFL, Duolingo or PTE and Standardized tests like SAT/ACT, GRE, GMAT, MCAT and LSAT. As taking these tests are an important obligation for international education. Make sure that you have taken your test with the required benchmark scores.
- Apply for the institution early. Have your intakes selected and know your application deadlines to apply. Receive the offer letter upon successfully applying for the institution.
- Complete the SEVIS process. You have to pay a mandated fee to the Student and Exchange Visitor Information System (SEVIS). This fee is different from the visa application fees.
- Apply for a study visa (F1, M1, or J1). Your program of study determines what study visa you must apply for.
- Find the nearest US embassy or consulate to apply for the international student visa. Make the visa application fee payment and file your visa application.
- Complete the visa interview – Schedule the interview at the nearest US embassy that you selected and wait for the call. Carry all the necessary documents. Once called, attend the interview, justify the reason for choosing your institution, program, and particularly the US.
- Receive your visa – You will be informed about your visa approval at the end of your interview and upon successful approval, you will receive it stamped within 3 to 7 days.
Visitor Visa

A USA visitor visa, also known as a B-2 visa, is a non-immigrant visa for individuals who wish to enter the United States temporarily for tourism, vacation, or visiting friends and family. Here’s the process of obtaining a USA visitor visa:
- Determine Eligibility: Ensure that you meet the eligibility criteria for a B-2 visa, which includes demonstrating that:
- Your trip is for tourism, visiting friends or family, medical treatment, or participation in social events.
- You plan to stay in the U.S. for a specific, limited period.
- You have a residence outside the U.S. and other binding ties that will ensure your return at the end of your visit.
- You have sufficient funds to cover your expenses while in the U.S.
- Complete Form DS-160
- Fill out the Online Non-immigrant Visa Application (Form DS-160)
- Pay the Visa Fee
- Pay the non-refundable visa application fee. The fee is typically $160 but can vary depending on your country of origin.
- Schedule an Interview
- Schedule an appointment for a visa interview at the U.S. Embassy or Consulate in your country. Wait times for interview appointments can vary, so it’s best to apply well in advance of your travel date.
- Gather Required Documentation– Prepare the following documents for your interview:
- Valid passport with at least six months validity beyond your intended stay in the U.S.
- Form DS-160 confirmation page.
- Visa application fee payment receipt.
- Photo (if the upload fails, bring one to the interview).
- Appointment confirmation letter.
- Documents demonstrating the purpose of your trip, your intent to depart the U.S. after your trip, and your ability to pay all costs of the trip.
- Attend the Visa Interview During the interview, a consular officer will ask you questions about your trip and your ties to your home country. Be prepared to discuss your travel plans, your employment, family ties, and reasons for returning home. The officer will also take your fingerprints during the interview.
- Additional Documentation (if requested)-You may be asked to provide additional documentation such as:
- Evidence of your employment or studies.
- Bank statements or other financial documents.
- A letter of invitation from friends or relatives in the U.S. if applicable .
- Wait for Visa Processing-After the interview, your application may undergo administrative processing, which can take additional time. If your visa is approved, you will be informed how your passport with the visa will be returned to you (typically via courier).
USA Work Permit
A USA work permit, also known as an Employment Authorization Document (EAD), allows non-citizens to legally work in the United States. Here’s the process and requirements for obtaining a work permit:
- Eligibility: You qualify if authorized under your immigration status, have a pending work-related application, or need explicit authorization on an existing work visa.
- Form I-765: Complete the Application for Employment Authorization (Form I-765) online or on paper.
- Documentation: Include proof of eligibility, passport photos, Form G-28 if represented by an attorney, and previous EAD if renewing.
- Filing Fee: Pay the $410 filing fee (varies by category) and possibly an $85 biometric services fee. Fee waivers may apply.
- Application Submission: Submit Form I-765, documentation, and fees to the appropriate USCIS service center based on your eligibility and residence.
- Biometrics Appointment: Attend if required for fingerprinting, photograph, and signature.
- Processing: USCIS processes applications, with varying timelines.
- EAD Receipt: Upon approval, USCIS mails your Employment Authorization Document (EAD) as proof of work authorization.
Renewal or Replacement
- Renew before expiry, submit up to 180 days early. Replace if lost, stolen, or damaged.
Specific Eligibility Categories
- Students (F-1) for OPT or CPT, H-4 spouses under conditions, Asylees, Refugees, DACA recipients, and TPS holders.



